Converts incoming x-ray photons to electrical digital signal through an x-ray photoconductor. Direct detectors convert from the x-rays electrons that are measured whereas indirect detector convert from x-rays to visible light first and then to electrons that.

Direct Digital Radiography Or Direct Capture Radiography Ppt Download
Indirect imaging systems however record the image using the information produced at the output phosphor of an image intensification device.
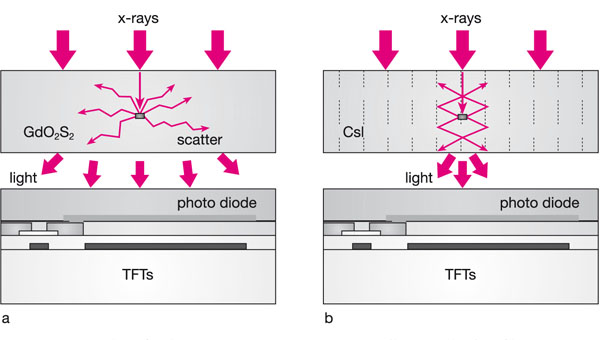
. These systems use amorphous selenium and a TFT. Direct radiography is subdivided into direct conversion that uses a flat panel detector and indirect conversion that involves a flat panel detector and indirect conversion with a charged couple device detector CCD. Advantages and disadvantages of digital radiology.
DR uses flat panel detectors. There are two primary methods of conversion either indirect or direct. Direct digital radiography DDR refers to direct digital registration of the image at the detector with no intermediate processing step required to obtain the digital signals as in computed radiography CR.
A computer program is essential to construct the image in all digital imaging. Types of Digital Imaging Direct digital imaging Indirect digital imaging Storage phosphor imaging The difference between each method is in how the image is obtained and in what size the receptor plates are available eg panoramic. Direct Digital Radiography DR Type of digital radiography in which detector and reader are permanent part of table or wall unit.
Whereas the Transit Method is prone to false positives in up to 40 of cases involving. The incident x-ray radiation is converted into an equivalent electric charge and then to a digital image through a detector sensor. The term flat-panel detector is also being used to describe both the indirect amorphous silicon and the direct amorphous selenium plates that are being used in some digital systems.
Digital radiography is an advanced form of radiography that uses x-ray sensitive plates to capture data during article examination which is immediately transferred to a computer without the use of an intermediate cassette. The x-rays are captured by a radiation-sensitive circuit board which automatically generates the image and sends it directly to the computer. The direct digital equipment works similar to the indirect equipment the difference is that it is not necessary to use the digital plate nor the reader of this plate.
In direct digital imaging x-rays interact directly with the element selenium creating an electric charge. Digital dental images are acquired through three methods. Here you have two antibodies primary and secondary.
The primary antibody binds to a binding site of your target protein whereas the secondary antibody binds to the primary one. Converts incoming x-ray photons to electrical digital signal through a x-ray photoconductor. Indirect imaging systems Rapid serial radiographic systems produce the image through the direct interaction of the x-radiation with the screenfilm system.
Explain the difference between analog and digital data and differentiate between direct and indirect digital imaging. Converts incoming x-ray photons to light through a scintillation and then converts the light to electrical digital signal through a photodiode or CCD. Direct digital techniques often known as DR or digital radiography refer to sensors that send a digital image straight to a computer whereas indirect digital techniques involve scanning reusable phosphor-coated plates to obtain a digital image which.
FPD can be divided into two categories. Direct DR systems are capable of directly converting incoming x-ray photons to an electronic signal. Computers require an electric signal to generate a visible image.
Direct digital imaging does not require a light-emitting phosphor. Indirect digital uses reusable phosphor coated plates that are run through a scanner to obtain the digital image which. CR has been known as an indirect digital technology bridging the gap between x-ray film-based and fully digital detectors.
By Brian Nett PhD X-Ray Physics. Converts incoming x-ray photons to light through a scintillation and then converts the light to electrical digital signal through a photodiode or CCD. The direct method indirect method and semi-indirect method.
Digital radiography detectors are used to directly acquire x-ray images in place of film or computed radiography CR systems and are separated into direct and indirect detectors. One of the most obvious advantages of Direct Imaging is that it is less prone to false positives. Digital radiography is a type of X-ray imaging that uses digital X-ray sensors to replace traditional photographic X-ray film producing enhanced computer images of teeth gums and other oral structures and conditions.
Computed Radiography CR Type of indirect digital radiography tech must move detector between image acquisition and display monitor. Direct digital refers to sensors that send a digital image directly to a computer and is also knows as DR or digital radiography. Both computed radiography CR and digital radiography DR require the use of digital technologies which rely on computer networks and high-bandwidth web facilities.
Compare and contrast digital imaging receptors. Most hospitals in India are going for the X-Ray CR System combination calling it digital X-Ray since this is far more cost-effective digital filmless and eliminates the cumbersome hazardous dark-room development. List the basic components of a digital imaging system and outline the advantages and disadvantages of digital imaging versus film-based imaging.
Indirect capture digital radiography devices absorb x-rays and convert them into light. Indirect capture and direct capture.

Indirect And Direct Conversion Digital Radiography Basics Youtube

Digital Radiography Flashcards Quizlet

0 Comments